How To Create An App Without Experience
Intro
I was recently tasked with building two applications in parallel. The first was a commercial web application, and the second acted as a platform to A/B test content messaging, page layouts, and so on.
To be ruthlessly efficient, I wanted to reuse the majority of the core components and styles for both applications, and interchange any branded assets (images, fonts, color palette, etc.) with a dummy brand using Styled Components' theming capabilities.
The challenge, then, was to create multiple applications from a single create-react-app (CRA) application that shared common components and styles but with no trace of the other's branded assets in their bundled build files. Thankfully, there's a number of ways to achieve this, ranging in complexity and development effort.
Multiple options for multiple entry points
Lerna is a popular tool that maintains multiple packages under a single repository (commonly referred to as a monorepo). It achieves this by linking identical dependencies across its packages, with the ability to publish them either collectively or individually.
Lerna would allow us to create a package for each application and one for the core components to share between them. This certainly solves the use case, but requires us to rearchitect the entire codebase and increase the complexity of the build process.
Given that there are no immediate plans to add any other containers to the codebase, and that the testing application will likely not be required beyond the initial development phases, we decided the associated overhead for this scenario was overkill.
A leaner approach would be to rewire the codebase with React App Rewired, which tweaks the CRA build scripts without having to eject. In our case, we would use rewired to alter the application's entry point at build time.
A major drawback here is that in doing so, we'd break the guarantees that CRA provides by hiding the configuration files from us, and the software itself is only lightly maintained by the community at the time of writing (customize-cra is a popular package built on top of rewired that supports CRA v2).
This solution could be viable on a personal project, but it wasn't something we were willing to depend on for a commercial application.
Ejecting is a one-way operation that cannot be undone. It allows us complete control of the project's infrastructure by converting the codebase into a standard React application at the cost of transferring the responsibility of maintaining the exposed configuration to our team.
This option is viable in some scenarios, but it's usually considered a last resort due to the increased complexity and associated maintenance cost.
Each of these — and plenty more — are all viable solutions that come with their own set of benefits and drawbacks. However, for this particular scenario, we were keen to investigate a simple solution that allows us to work from a single codebase, not rely on third-party dependencies, and not eject from the safety net of CRA.
To infinity, or beyond
Let's look at the default entry point in a CRA application. The src/index.js file imports the App container and renders it inside the div#root element defined in public/index.html.
/* src/index.js */ import React from 'react'; import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'; import App from './App'; ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('root')); /* public/index.html */ <body> <noscript>You need to enable JavaScript to run this app</noscript> <div id="root"></div> </body> We can introduce multiple points of entry by importing both containers into the index.js file and conditionally render them based on a constant variable. This allows us to switch between the containers, but comes with a couple of caveats.
In order to switch between the builds, we'd need to manually update the isTestEnv variable. The variable always needs to be correctly set when each of the sites are deployed, otherwise the wrong code would be deployed to the production environment.
/* src/index.js */ import React from "react"; import ReactDOM from "react-dom"; import App from "./app"; import Test from './test'; const isTestEnv = true; if (isTestEnv) { ReactDOM.render(<Test />, document.getElementById("root")); } else { ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById("root")); } Let's tighten this up by creating a .env file with a custom environment variable. Now we have the ability to choose the build target before running the local development script and also permanently assign a value to each of our production environments.
/* .env */ REACT_APP_BUILD_TARGET= /* index.js */ import React from "react"; import ReactDOM from "react-dom"; import { App } from "./App"; import { Test } from './Test'; if (process.env.REACT_APP_BUILD_TARGET === 'test') ReactDOM.render(<Test />, document.getElementById("root")); } else { ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById("root")); } We used Netlify to create a production environment for each application. Both sites will be virtually identical. They'll both point to the same GitHub repository and have master set as the production branch. The only difference will be their respective BUILD_TARGET environment variable: test is assigned to the testing site, and app for the main application.
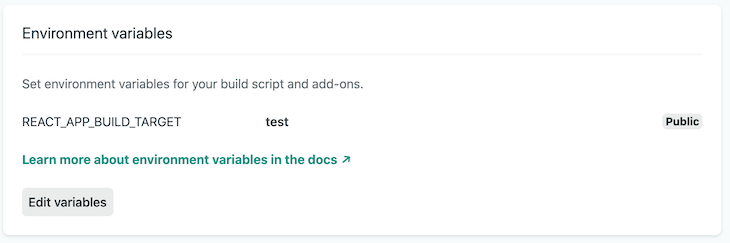
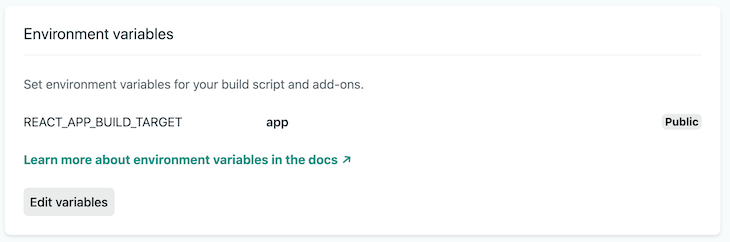
We now have two production environments with the correct build target and free from human error. All that's left is to ensure that only the code from the defined container appears in the bundled build.
Due to the nature of tree shaking, all of the imported containers in the application's current index.js file would appear in the production build files, regardless of our build target. To remedy this, we can use CommonJS to conditionally require the desired container based on the BUILD_TARGET environment variable.
/* index.js */ require(process.env.REACT_APP_BUILD_TARGET === "test" ? "./test" : "./app" );
This works, but setting the environment variable to anything other than test will import the main application. We can fix this with an if/else statement and further refine the solution with ES6 dynamic imports.
The importBuildTarget() function below will return a promise for each entry point and a fallback error in the event that the specified build target is not found. Once the import promise has resolved, it will render the requested build target with none of the other entry point files in the bundled build. 💥
/* index.js */ import React from "react"; import ReactDOM from "react-dom"; function importBuildTarget() { if (process.env.REACT_APP_BUILD_TARGET === "app") { return import("./app.js"); } else if (process.env.REACT_APP_BUILD_TARGET === "test") { return import("./test.js"); } else { return Promise.reject( new Error("No such build target: " + process.env.REACT_APP_BUILD_TARGET) ); } } // Import the entry point and render it's default export importBuildTarget().then(({ default: Environment }) => ReactDOM.render( <React.StrictMode> <Environment /> </React.StrictMode> , document.getElementById("root") ) ); TL; DR
You can create multiple entry points in a CRA application without ejecting by using an environment variable to conditionally import container files. Doing this prevents code from the other containers appearing in the desired bundled build.
Resources
- GitHub: https://github.com/phunkren/multiple-entry-points
- Entry point A: https://multiple-entry-points-app.netlify.app
- Entry point B: https://multiple-entry-points-test.netlify.app
Special thanks to Stephen Taylor and Robin Weston for their valuable input, and to Jonathan Hawkes for his solution to all build target files appearing in the bundled build.
Like the article? Let me know on Twitter 🐦
Full visibility into production React apps
Debugging React applications can be difficult, especially when users experience issues that are hard to reproduce. If you're interested in monitoring and tracking Redux state, automatically surfacing JavaScript errors, and tracking slow network requests and component load time, try LogRocket. 
LogRocket is like a DVR for web apps, recording literally everything that happens on your React app. Instead of guessing why problems happen, you can aggregate and report on what state your application was in when an issue occurred. LogRocket also monitors your app's performance, reporting with metrics like client CPU load, client memory usage, and more.
The LogRocket Redux middleware package adds an extra layer of visibility into your user sessions. LogRocket logs all actions and state from your Redux stores.
Modernize how you debug your React apps — start monitoring for free.
How To Create An App Without Experience
Source: https://blog.logrocket.com/multiple-entry-points-in-create-react-app-without-ejecting/
Posted by: geistfairie.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Create An App Without Experience"
Post a Comment